
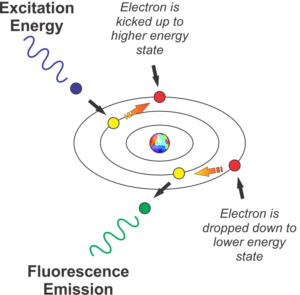
The schematic representation of the fluorescence effect below demonstrates the mechanism when blue light strikes the protein GFP, which absorbs the blue light’s energy. The absorption of the light’s energy causes the electrons of the protein’s constituent atoms to make a quantum jump from one valence electron shell to a higher shell. This change of energy state then effectively, instantly “decays” back to its quiescent resting state. When the decay occurs, the electron gives up or emits, a photon of light, but at a lower energy and longer wavelength because a minuscule amount of heat is given up in this process as well through the concept of conservation of energy. This is quantum mechanics (QM) at work here! QM is a term that is misused and abused in many articles relating to pseudoscience but this is one example of QM that you can witness with your eyes in real time.
In summary, when you illuminate the protein with blue light, it emits back in other colors of the spectrum, including green, yellow, orange, and red. The color emitted is determined by how many jumps the electron makes.
Copyright 2012 Lynn Miner
If you have any questions, comments or suggestions – PLEASE don’t hesitate to contact us.